Understanding Dog Eye Discharge
Dog eye discharge is a natural protective mechanism your pet’s eyes use to remove debris and maintain proper lubrication. Just like humans, dogs produce tears to keep their eyes clean and healthy. This discharge can range from normal moisture to concerning secretions that signal underlying health issues.
Types of Dog Eye Discharge:
- Clear and Watery: Normal tear production, potential allergic reactions, response to environmental irritants
- White-Gray and Mucus-Like: Morning eye boogers, dust accumulation, mild irritation
- Yellow or Green Discharge: Bacterial infections, possible conjunctivitis, signs of serious eye conditions
- Reddish-Brown Tear Stains: Common in light-colored dogs, can indicate excessive tearing, might signal tear duct problems
Your dog’s eye discharge color and consistency provide valuable clues about their eye health. Clear tears are typically normal, while colored or thick discharge often indicates a problem requiring attention. Breeds with prominent eyes or flat faces like Shih Tzu tend to experience more discharge due to their facial structure and hair.
A sudden change in your dog’s eye discharge pattern warrants closer monitoring. Understanding these variations helps you identify when your pet needs veterinary care at clinics like Petyaari Pet Clinic.
Common Causes of Dog Eye Discharge
Your dog’s eye discharge can stem from various underlying conditions:
1. Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
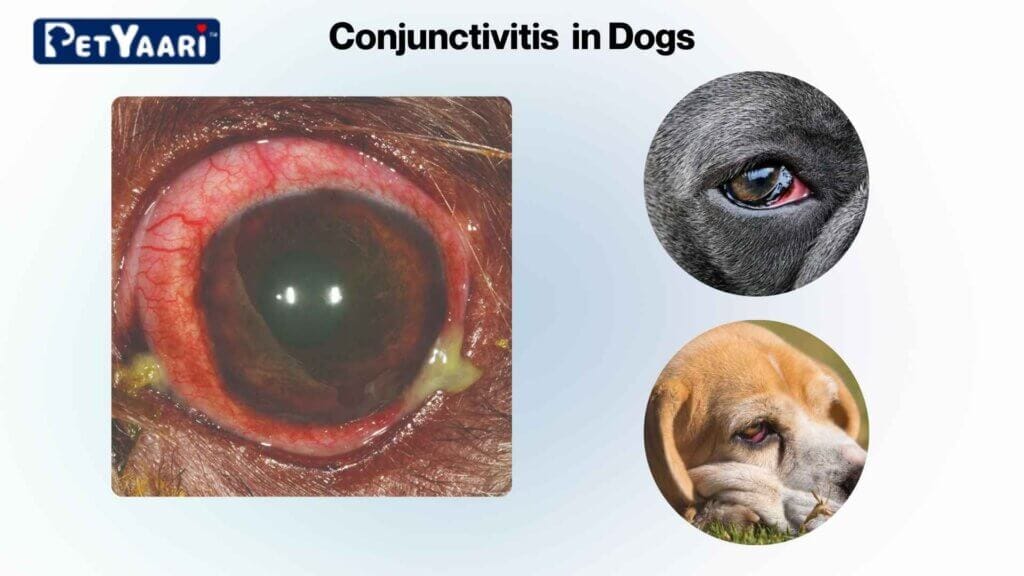
- Bacterial infections causing redness and inflammation
- Viral infections spreading between dogs
- Environmental irritants triggering inflammation
2. Allergic Reactions
- Pollen and seasonal allergens
- Household cleaning products
- Dust and smoke exposure
3. Physical Irritants
- Dirt or debris trapped under eyelids
- Scratches from plant material
- Hair rubbing against cornea
4. Structural Issues
- Blocked tear ducts preventing proper drainage
- Tear film deficiency leading to dry eyes
- Eyelid abnormalities affecting tear distribution
5. Breed-Specific Problems
- Nodular episcleritis in Collies
- Brachycephalic breeds (Pugs, Bulldogs) prone to eye issues
- Entropion in Shar-Peis causing eyelash irritation
6. Serious Medical Conditions
- Glaucoma causing pressure buildup
- Corneal ulcers damaging eye surface
- Systemic infections affecting eye health
7. Parasitic Infections
- Eye worms requiring immediate treatment
- Mange mites affecting eyelids
- Tick-borne diseases impacting eye health
Symptoms to Watch For Dog Eye Discharge
Identifying eye discharge symptoms early helps prevent serious complications in your dog’s eye health. Watch for these key signs:
- Excessive Blinking or Squinting: Your dog might keep one or both eyes partially closed
- Pawing at Eyes: Repeated attempts to scratch or rub the affected area
- Visible Swelling: Puffy appearance around the eye area
- Eye Redness: Bloodshot appearance in the white part of the eye
- Changes in Behavior: Increased sensitivity to light or reluctance to play
Unilateral vs. Bilateral Symptoms
- Single Eye (Unilateral): Often indicates injury or foreign object
- Both Eyes (Bilateral): Typically suggests allergies or systemic conditions
The color and consistency of discharge provide valuable diagnostic clues:
- Clear and Watery: Points to allergies or early infection
- Thick and Yellow-Green: Signals potential bacterial infection
- Crusty Build-up: May indicate chronic condition needing attention
Your dog might also display subtle signs like keeping their head tilted or showing reluctance to let you examine the affected eye. These behavioral changes warrant closer observation and potential veterinary evaluation.
Diagnosing the Cause of Dog Eye Discharge
Professional veterinary diagnosis is essential for identifying the root cause of eye discharge in dogs. At Petyaari Pet Clinic, veterinarians use specialized diagnostic tools and methods to determine the specific condition affecting your pet.
The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Physical Examination: A thorough inspection of the eye structure, surrounding tissues, and discharge characteristics
- Fluorescein Staining: A special dye test to detect corneal ulcers or scratches
- Schirmer Tear Test: Measures tear production to identify dry eye conditions
- Culture Samples: Identifies specific bacterial or fungal infections
- Pressure Testing: Checks for glaucoma when suspected
Self-diagnosis can lead to incorrect treatment choices and potentially worsen the condition. Certain symptoms might appear similar but require different treatments – bacterial infections and allergies can present similar signs yet need distinct therapeutic approaches.
Advanced cases might require additional diagnostic procedures:
- Digital imaging
- Ultrasound examination
- Blood tests to check for underlying systemic conditions
These comprehensive diagnostic methods ensure accurate treatment plans tailored to your dog’s specific condition.
Treatment Options for Dog Eye Discharge Based on Cause
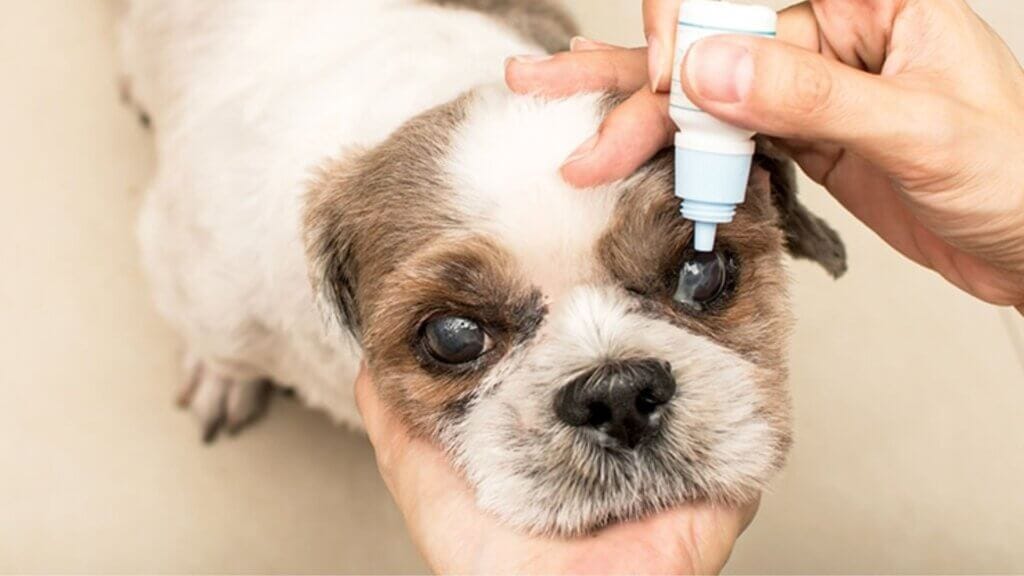
Your veterinarian will prescribe specific treatments based on the underlying cause of your dog’s eye discharge. Here’s what you can expect for different conditions:
Bacterial Infections
- Antibiotic eye drops or ointments applied 3-4 times daily
- Oral antibiotics for severe cases
- Treatment typically lasts 7-14 days
Allergic Reactions
- Antihistamine medications to reduce inflammation
- Sterile saline eye wash to flush irritants
- Prescription eye drops to manage symptoms
Foreign Body Removal
- Local anesthetic drops for minor cases
- Sedation for deeply embedded objects
- Post-removal antibiotic drops to prevent infection
Blocked Tear Ducts
- Surgical procedure to open blocked ducts
- Post-operative medications
- Regular follow-up checks to ensure proper drainage
Protective Measures During Treatment
- Elizabethan collar to prevent scratching
- Regular cleaning with prescribed solutions
- Keeping the eye area dry and debris-free
The success of treatment depends on accurate diagnosis and consistent application of prescribed medications. Your dog might need multiple treatments or adjustments to their medication depending on how they respond to initial therapy.
Home Remedies and Care Tips for Dog Eye Infections
You can support your dog’s eye health at home with several safe care measures while following your vet’s treatment plan:
- Apply Cold Compresses: Use a clean, damp cloth cooled in the refrigerator to reduce swelling and discomfort. Hold it gently against your dog’s eye for 5-10 minutes.
- Maintain Eye Hygiene:
- Trim facial hair around the eyes to prevent irritation
- Clean discharge with sterile saline solution
- Use separate clean cloths for each eye to prevent cross-contamination
- Create a Safe Environment:
- Keep your home dust-free
- Avoid smoking near your pet
- Remove potential eye irritants from your dog’s height level
Important Safety Notes:
- Stop home treatment if symptoms worsen
- Never use human eye drops on dogs
- Seek immediate veterinary care for:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Changes in eye color
- Visible injuries
- Persistent discharge despite home care
These home remedies work best as complementary care alongside professional treatment, not as replacements for veterinary intervention.
Preventive Measures to Maintain Healthy Eyes in Dogs
Regular eye care prevents infections and maintains your dog’s ocular health. Here’s what you need to do:
- Daily Eye Checks: Inspect your dog’s eyes each morning for redness, cloudiness, or discharge
- Clean Eye Area: Wipe the area around the eyes with a damp, clean cloth daily
- Trim Facial Hair: Keep long hair around eyes trimmed to prevent irritation
- Protect During Grooming: Use pet-safe shampoos and shield eyes during baths
- Car Safety: Keep car windows up during rides to protect eyes from debris
- Breed-Specific Care: Flat-faced breeds need extra attention due to protruding eyes
- Environmental Control: Minimize exposure to dust, smoke, and strong winds
Schedule regular check-ups at Petyaari Pet Clinic every 6 months for professional eye examinations. Your veterinarian can detect early signs of breed-specific conditions and provide preventive treatments before problems develop.
Maintain a clean living environment and keep your dog’s bedding fresh to reduce exposure to allergens and irritants that could affect eye health.
When to Consult a Veterinarian at Petyaari Pet Clinic
Don’t wait for eye problems to get worse – seek professional care at the first sign of persistent discharge or discomfort. Petyaari Pet Clinic’s experienced veterinarians use advanced diagnostic tools to identify and treat eye conditions effectively.
Schedule an immediate consultation if you notice:
- Discharge lasting more than 24 hours
- Changes in eye color or cloudiness
- Squinting or excessive blinking
- Visible swelling or redness
- Signs of pain or discomfort
Petyaari Pet Clinic offers specialized treatment protocols for various eye conditions, including conjunctivitis and breed-specific issues. Early intervention prevents serious complications like vision loss or permanent eye damage. Our team provides comprehensive care, from initial diagnosis through complete recovery.
Contact Petyaari Pet Clinic today to protect your dog’s eye health.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the different types of dog eye discharge and what do they indicate?
Dog eye discharge can vary in type including clear, watery, or yellow-green pus-like. Clear or watery discharge often indicates allergies or irritation, while yellow-green pus-like discharge usually suggests a bacterial infection or conjunctivitis.
What are the common causes of eye discharge in dogs?
Common causes include conjunctivitis (pink eye), allergies, foreign bodies irritating the eye, tear film deficiency, obstructed tear ducts, parasitic infections, injuries, breed-specific conditions like nodular episcleritis in Collies or brachycephalic breed issues, and serious conditions such as glaucoma and corneal ulcers.
What symptoms should I watch for if my dog has eye discharge?
Symptoms to watch for include itching, pawing at the eye, frequent blinking or squinting, redness and swelling around the eyes. It’s important to note whether symptoms affect one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral) to help determine the underlying cause.
How is the cause of dog eye discharge diagnosed?
Professional veterinary evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis. Methods include physical examination, tear tests, cultures, and imaging if necessary. Self-diagnosis is risky as similar symptoms can have different causes requiring specific treatments.
What treatment options are available for dog eye discharge based on its cause?
Treatment varies by cause: antibiotics and medicated eye drops for bacterial infections; antihistamines for allergies; removal of foreign bodies under sedation if needed; surgery for blocked tear ducts followed by medication; and use of Elizabethan collars to prevent rubbing during healing.
When should I consult a veterinarian at Petyaari Pet Clinic for my dog’s eye discharge?
Early professional intervention is crucial to prevent complications like permanent damage or vision loss. If symptoms persist or worsen despite home care, it’s important to seek expert advice at Petyaari Pet Clinic where specialized diagnostic tools and treatment protocols are available.
